| Community Monitoring in Health Resources for the Practitioner |
|
Strategies to Build Relationship
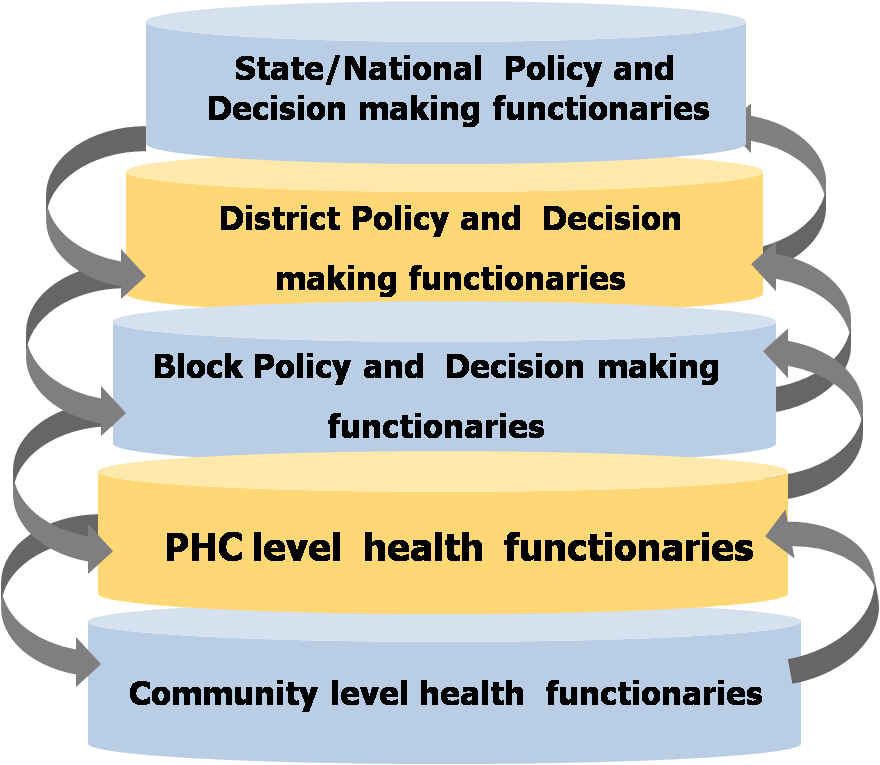
It is important for the community to note that all the levels are inter-related and the levels of power and authority are different. In practical terms very less authority, power, resources and very high burden of work is at the lowest level where the contact and expectations of the community is highest. At the higher levels authority and policy making decisions are taken but the engagement of the community is very less. It is crucial for the community to understand this power dynamics between the health functionaries at different levels. While for the proper dispensation of medicines which are supplied, the community has to engage at the primary care level. However, for policy decisions such as increasing the supply of medicines, increasing budget, supplying adequate and appropriate medicines as per the local need, engagement has to continue at the higher levels. Hence, relationship building at all levels, critical engagement at all levels and differential engagement at different levels is very essential.It is important to note that whatever change occurs at the lower most level, it is often the outcome of the critical and strategic engagement at various levels. The various strategies:
|
Levels of Community Engagement for
Feedback & Action |